

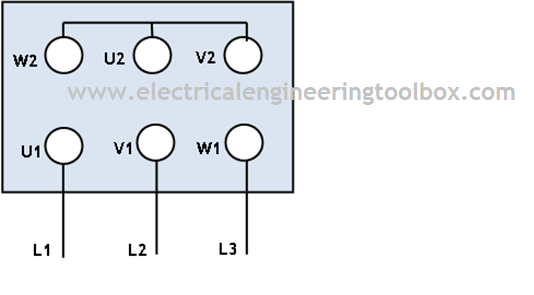
Repeat this test by either switching the lead wires or switching the direction of rotation of the back-driven motor. While the motor is being back-driven, apply a voltage to the terminals (again, until the current reads 25% of rated full load current). This method requires you to back drive your test motor at a slow speed. The second method requires only 2 measurements but it is a little more complicated test setup. Repeat this a number of times at different locked rotor positions and then take the average resistance. Using that voltage and current, determine resistance using Ohm's Law. You increase the voltage until the current is at 25% of the rated full load current. There are 2 ways to measure terminal resistance.įirst, you can lock the rotor of the motor and apply voltage to the terminals. You mention that you are measuring "internal resistance" which is often exclusive of the lead wires and brushes (i.e., it is measured from bar to bar on the armature). You should be measuring terminal resistance (resistance from one lead wire to the other lead wire) for IR compensation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
